ChatGPT Atlas represents a significant advancement in the realm of generative AI and its impact on search engine optimization (SEO). This comprehensive overview explores the multifaceted nature of ChatGPT Atlas, its foundational technologies, diverse applications, and its role in reshaping how content interacts with generative search engines.
The Foundation of ChatGPT Atlas
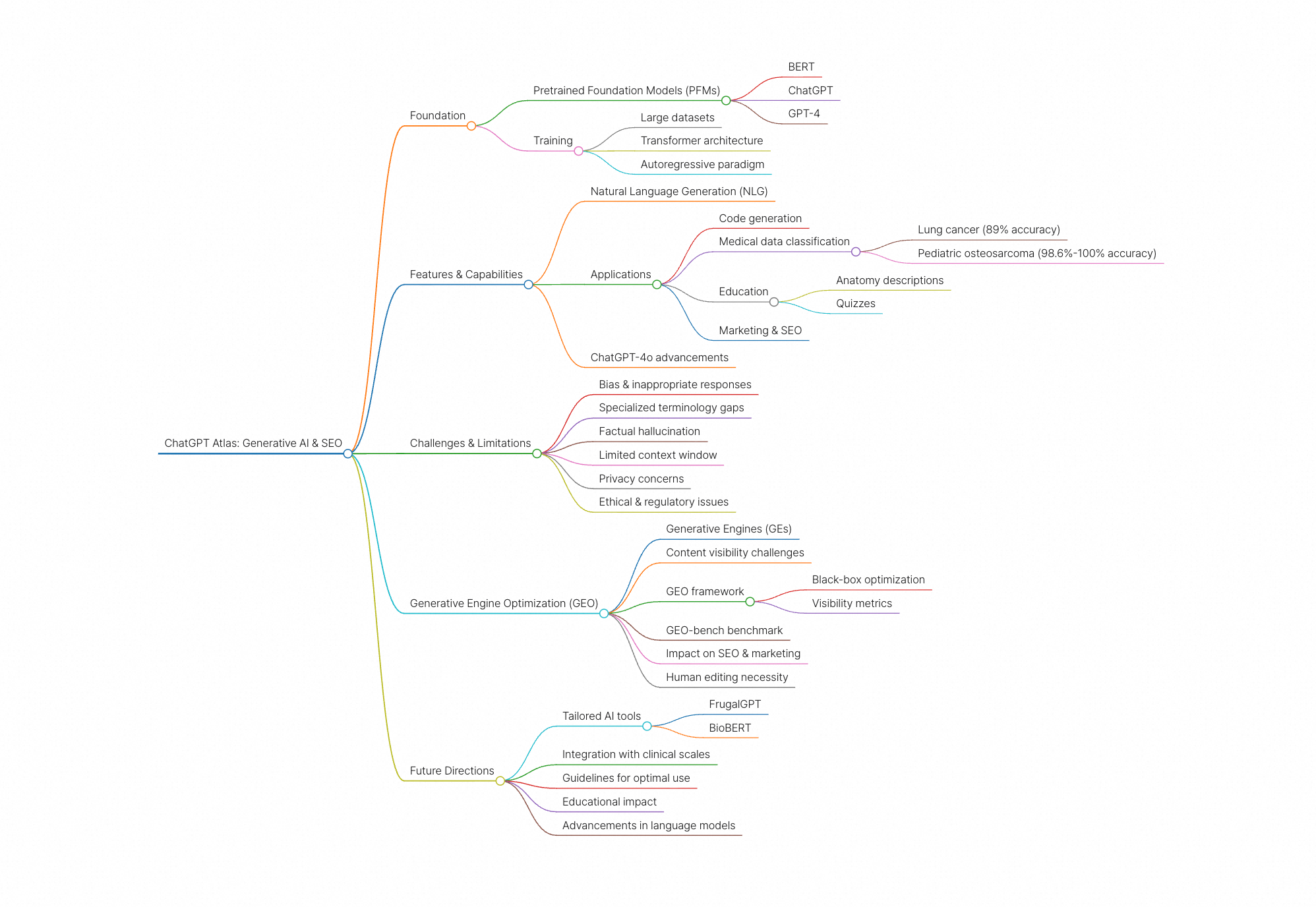
ChatGPT Atlas is built upon the powerful architecture of Pretrained Foundation Models (PFMs), which are designed to be the bedrock for various tasks across different data types. These models, including BERT, ChatGPT, and GPT-4, are trained on extensive datasets to provide a strong parameter initialization for a wide array of downstream applications. Unlike older methods that relied on convolution and recurrent modules for feature extraction, models like BERT learn bidirectional encoder representations from Transformers, trained on large datasets as contextual language models. Similarly, the Generative Pretrained Transformer (GPT) family, which ChatGPT is a part of, utilizes Transformers as feature extractors and is trained on large datasets using an autoregressive paradigm.
ChatGPT, specifically, has gained significant recognition for its success in large language models, employing autoregressive language models with zero-shot or few-shot prompting capabilities. This enables it to engage in interactive conversations, answer questions, and provide information in a natural manner. The system is trained on massive amounts of text data and uses an attention mechanism to comprehend language structure and generate coherent and relevant responses. The exceptional performance of PFMs has led to substantial breakthroughs in AI, driving numerous studies and increasing the demand for updated surveys on their capabilities and applications.
Features and Capabilities of ChatGPT
ChatGPT is a sophisticated AI-based Natural Language Generation (NLG) system that allows users to interact with virtual agents conversationally. Developed by OpenAI, this language model, often based on the GPT-3.5 architecture, has garnered widespread attention for its ability to produce human-like responses to natural language inputs. It can provide quick and accurate responses to a broad spectrum of user queries due to its training on a massive corpus of text data.
The capabilities of ChatGPT extend across various domains. It can generate fully functional computer code, answer simple questions, and assist in creating interactive plotting tools for engineering problems. In the medical field, ChatGPT-3.5 has demonstrated the ability to extract pathological classifications from lung cancer datasets with an overall accuracy of 89%, outperforming traditional NLP methods. For pediatric osteosarcoma datasets, it accurately classified both grades and margin status with accuracies of 98.6% and 100% respectively. These results highlight the feasibility of using ChatGPT for processing large volumes of clinical notes for structured information extraction without requiring extensive task-specific human annotation and model training.
Furthermore, ChatGPT has potential applications in education, marketing, and creative writing. It can serve as a valuable educational tool, especially in anatomy education, by providing accurate and well-structured anatomical descriptions, offering concise summaries, and generating multiple-choice quizzes. However, it is acknowledged that ChatGPT cannot replace the critical role of educators and should be used as a complementary tool. In marketing communications and SEO, ChatGPT offers benefits such as enhanced creativity, efficiency, and customer engagement. The recently launched ChatGPT-4o offers unique technological advancements that are expected to have a profound impact on fields like English Language Teaching (ELT).
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its impressive capabilities, ChatGPT is not without its limitations and challenges. One significant concern is its propensity to generate biased or inappropriate responses, which stems from the input data it was trained on. Its reliance on statistical patterns in text data also means it may struggle with more nuanced or complex language tasks.
In healthcare applications, while ChatGPT can be useful, most misclassifications in pathology report extraction were due to a lack of highly specialized pathology terminology and erroneous interpretation of staging rules. Additionally, ChatGPT has limitations such as a lack of common sense knowledge, a tendency for factual hallucination, a restricted context window, and potential privacy concerns. In anatomy education, while it provides accurate descriptions, its replies regarding anatomical variants and their clinical significance were found to be inadequate unless variants were systematically classified.
Moreover, the ethical and regulatory issues surrounding ChatGPT's use, especially given its training on vast amounts of human-generated text, raise questions about its accuracy. These concerns underscore the need for ongoing research into model interpretability, common-sense reasoning, and handling of longer context windows to fully realize the potential of LLMs like ChatGPT.
ChatGPT Atlas and Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
The advent of large language models (LLMs) has led to a new paradigm in search engines, where generative models are used to gather and summarize information to answer user queries. These Generative Engines (GEs) can produce accurate and personalized responses, potentially replacing traditional search engines. While this shift improves user utility and generative search engine traffic, it presents a considerable challenge for content creators and website owners. The black-box and rapidly evolving nature of generative engines means content creators have limited control over how and when their content is displayed.
To address this, Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) has been introduced as a new paradigm to help content creators enhance their content's visibility in generative engine responses. This framework allows for flexible black-box optimization and the definition of visibility metrics. GEO-bench, a large-scale benchmark of diverse user queries and relevant web sources, has been developed to facilitate systematic evaluation. Through rigorous testing, GEO has shown the capability to boost visibility by up to 40% in generative engine responses, though the efficacy of these strategies can vary across domains, necessitating domain-specific optimization methods.
The integration of AI tools like ChatGPT into marketing communications and Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is becoming increasingly important. ChatGPT can revolutionize search experiences, transform how information is generated and presented, and establish new access points for online engagement. These advancements are expected to significantly influence traditional search engine products, driving rapid industry innovation. However, challenges remain, such as maintaining content quality, addressing ethical dilemmas, and ensuring data privacy.
SEO, a crucial aspect of online visibility, involves optimizing web pages or entire sites to make them more search engine friendly and achieve higher rankings in search results. This includes designing, writing, and coding a website to improve the volume and quality of traffic from search engines. Generative AI in content SEO work is still largely unstructured and driven by individuals. While AI-generated text can be suitable for specific use cases, human edits and revisions are often necessary due to issues like text fluffiness, factual errors, incorrect tone, and mistrust in search engine guidelines. Despite these challenges, AI is seen as having the potential to replace human tasks, particularly in content ideation.
The Future of ChatGPT Atlas
The continuous evolution of generative AI models, including ChatGPT, signals a promising future for various fields, particularly in research and digital transformation. There is a growing focus on developing tailored AI tools to address domain-specific needs, as seen with advancements like FrugalGPT and BioBERT. The integration of AI models like AtlasGPT with clinical scales demonstrates promise in enhancing outcome prediction in medical scenarios.
Future research is expected to focus on establishing guidelines for ChatGPT's optimal use and application, especially in fields like medical education. As the technology advances, more sophisticated language models with greater capabilities and fewer limitations are anticipated. The educational impact of generative AI, particularly ChatGPT, is receiving significant attention, and understanding the types of knowledge teachers need to effectively use these tools is crucial. Overall, ChatGPT Atlas and similar generative AI tools are poised to continue transforming how we interact with information, solve complex problems, and optimize online content.